Streptococcus
| Streptococcus | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Firmicutes |
| Class: | Bacilli[1] |
| Order: | Lactobacillales |
| Family: | Streptococcaceae |
| Genus: | Streptococcus Rosenbach, 1884 |
| Species | |
|
S. agalactiae |
|
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria belonging to the phylum Firmicutes[2] and the lactic acid bacteria group. Cellular division occurs along a single axis in these bacteria, and thus they grow in chains or pairs, hence the name — from Greek στρεπτος streptos, meaning easily bent or twisted, like a chain (twisted chain). Contrast this with staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes and generate grape-like clusters of cells. Streptococci are oxidase- and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes.
In 1984, many organisms formerly considered Streptococcus were separated out into the genera Enterococcus and Lactococcus.[3]
Contents |
Pathogenesis
In addition to streptococcal pharyngitis (or strep throat), certain Streptococcus species are responsible for many cases of meningitis, bacterial pneumonia, endocarditis, erysipelas and necrotizing fasciitis (the 'flesh-eating' bacterial infections). However, many streptococcal species are non-pathogenic. Indeed, Streptococci are a necessary ingredient in Emmentaler ("Swiss") cheese. Streptococci are also part of the normal commensal flora of the mouth, skin, intestine, and upper respiratory tract of humans.
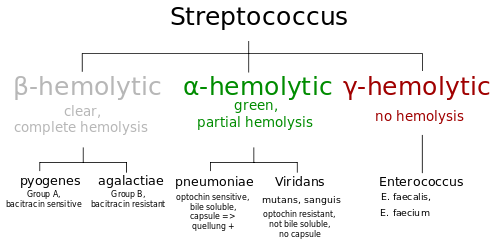
As a rule, individual species of Streptococcus are classified based on their hemolytic properties.[4] Alpha hemolysis is caused by a oxidation of iron in hemoglobin, giving it a greenish color on blood agar. Beta-only hemolysis is complete rupture of red blood cells, giving distinct, wide, clear areas around bacterial colonies on blood agar. Other streptococci are labeled as gamma hemolytic, actually a misnomer, as no hemolysis takes place.
Beta-hemolytic streptococci are further characterised via the Lancefield serotyping – based on specific carbohydrates in the bacterial cell wall.[5] These are named Lancefield groups A to v(except I and J), although some species, such as S. pneumoniae, do not express Lancefield antigens, but these are alpha-hemolytic not the beta-hemolytic to which this scheme refers. In the medical setting, the most important groups are the alpha-hemolytic streptococci, S. pneumoniae and Streptococcus Viridans-group, and the beta-hemolytic streptococci of Lancefield groups A and B (also known as “Group A strep” and “Group B strep”).
Alpha-hemolytic
Pneumococci
- S. pneumoniae, a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia and occasional etiology of otitis media, sinusitis, meningitis and peritonitis.
The Viridans group: alpha hemolytic and no Lancefield antigens
- S. mutans, a contributor to dental caries
- S. mitis, mostly found around cheek region
- S. sanguinis, no preference of locations
- S. salivarius, mostly found on the dorsal side of the tongue
- S. salivarius ssp. thermophilus, used in the manufacture of some cheeses and yogurts
- S. constellatus, occasional human pathogen, notable as colonies grown on blood agar smell strongly of caramel
Beta-hemolytic

Group A
S. pyogenes, also known as Group A Streptococcus (GAS), is the causative agent in Group A streptococcal infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis ("strep throat" AmE), acute rheumatic fever, scarlet fever, acute glomerulonephritis and necrotizing fasciitis. If strep throat is not treated, it can develop into rheumatic fever, a disease that affects the joints and heart valves. Other Streptococcus species may also possess the Group A antigen, but human infections by non-S. pyogenes GAS strains (some S. dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis and S. anginosus Group strains) appear to be uncommon.
Group A Streptococcus infection is generally diagnosed with a Rapid Strep Test (AmE) or by culture.
Group B
S. agalactiae, or GBS, causes pneumonia and meningitis in neonates and the elderly, with occasional systemic bacteremia. They can also colonize the intestines and the female reproductive tract, increasing the risk for premature rupture of membranes and transmission to the infant. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, American Academy of Pediatrics and the Centers for Disease Control recommend all pregnant women between 35 and 37 weeks gestation should be tested for GBS. Women who test positive should be given prophylactic antibiotics during labor, which will usually prevent transmission to the infant.[6] In the UK, clinicians have been slow to implement the same standards as the US, Australia and Canada. In the UK, only 1% of maternity units test for the presence of Group B Streptococcus.[7] Although The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists issued risk-based guidelines in 2003 (due for review 2006), the implementation of these guidelines has been patchy. Some groups feel that as a result over 75 infants in the UK die each year of GBS related disease and another 600 or so suffer serious infection, most of which could be prevented [8] however this is yet to be substantiated by randomized controlled trial in the UK setting and, given the evidence for the efficacy of testing and treating from other countries, it may be that the large-scale trial necessary would receive neither funding nor ethics approval.[9]
Group C
Includes S. equi, which causes strangles in horses,[10] and S. zooepidemicus - S. equi is a clonal descendent or biovar of the ancestral S. zooepidemicus - which causes infections in several species of mammals including cattle and horses.
Group D (enterococci) - variably hemolytic
Many former Group D streptococci have been reclassified and placed in the genus Enterococcus (including S. faecalis, S. faecium, S. durans, and S. avium).[11] For example, Streptococcus faecalis is now Enterococcus faecalis.
The remaining non-enterococcal Group D strains include Streptococcus bovis and Streptococcus equinus.
Group G streptococci
These streptococci are usually but not exclusively beta hemolytic. Streptococcus canis is an example of a GGS which is typically found on animals but can cause infection in humans.
Non-hemolytic
Non-hemolytic streptococci rarely cause illness. However, weakly hemolytic group D beta-hemolytic streptococci and Listeria monocytogenes (which is actually a gram positive bacillus) should not be confused with non-hemolytic streptococci.
Treatment
- See List of antibiotics.
See also
- Streptokinase
References
- ↑ "Result of detail taxonomy information". TXSearch Taxonomy Retrieval. DNA Data Bank of Japan. 19 February 2010. http://txsearch.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/txsearch/txsearch.TXSearch?tx_Clas=scientific+name&tx_Name=Streptococcus&tx_Rank=All&tx_Rmax=10&tx_Dcls=yes&tx_Lang=en&tx_Mode=DETAIL&tx_Id=1301&tx_R_Id=0. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ Ryan KJ, Ray CG, ed (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- ↑ Facklam R (October 2002). "What happened to the streptococci: overview of taxonomic and nomenclature changes". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15 (4): 613–30. doi:10.1128/CMR.15.4.613-630.2002. PMID 12364372. PMC 126867. http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12364372.
- ↑ Patterson MJ (1996). Streptococcus. In: Baron's Medical Microbiology (Baron S et al., eds.) (4th ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. (via NCBI Bookshelf) ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
- ↑ Facklam R (2002). "What happened to the streptococci: overview of taxonomic and nomenclature changes". Clin Microbiol Rev 15 (4): 613–30. doi:10.1128/CMR.15.4.613-630.2002. PMID 12364372.
- ↑ Schrag S, Gorwitz R, Fultz-Butts K, Schuchat A (2002). "Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease. Revised guidelines from CDC". MMWR Recomm Rep 51 (RR-11): 1–22. PMID 12211284.
- ↑ Hughes, RG, et al.. Prevention of Early Onset Neonatal Group B Streptococcal Disease. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. http://www.rcog.org.uk/index.asp?PageID=520.
- ↑ "Group B Strep Support Home Page". Group B Strep Support. 2007-01-09. http://www.gbss.org.uk/.
- ↑ "RCOG: Preventing group B streptococcus infection in new born babies". RCOG. 2006-02. http://www.rcog.org.uk/index.asp?PageID=1400#national.
- ↑ Harrington D, Sutcliffe I, Chanter N (2002). "The molecular basis of Streptococcus equi infection and disease". Microbes Infect 4 (4): 501–10. doi:10.1016/S1286-4579(02)01565-4. PMID 11932201.
- ↑ Ruoff KL (1990). "Recent taxonomic changes in the genus Enterococcus". Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 9 (2): 75–9. doi:10.1007/BF01963630. PMID 2108030.
External links
- Streptococcus genomes and related information at PATRIC, a Bioinformatics Resource Center funded by NIAID
- Prevention of Perinatal Group B Streptococcal Disease August 16, 2002 MMWR 2000;49:228-232.
- The Canadian Strep B Foundation
- The UK Group B Strep Support charity
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||